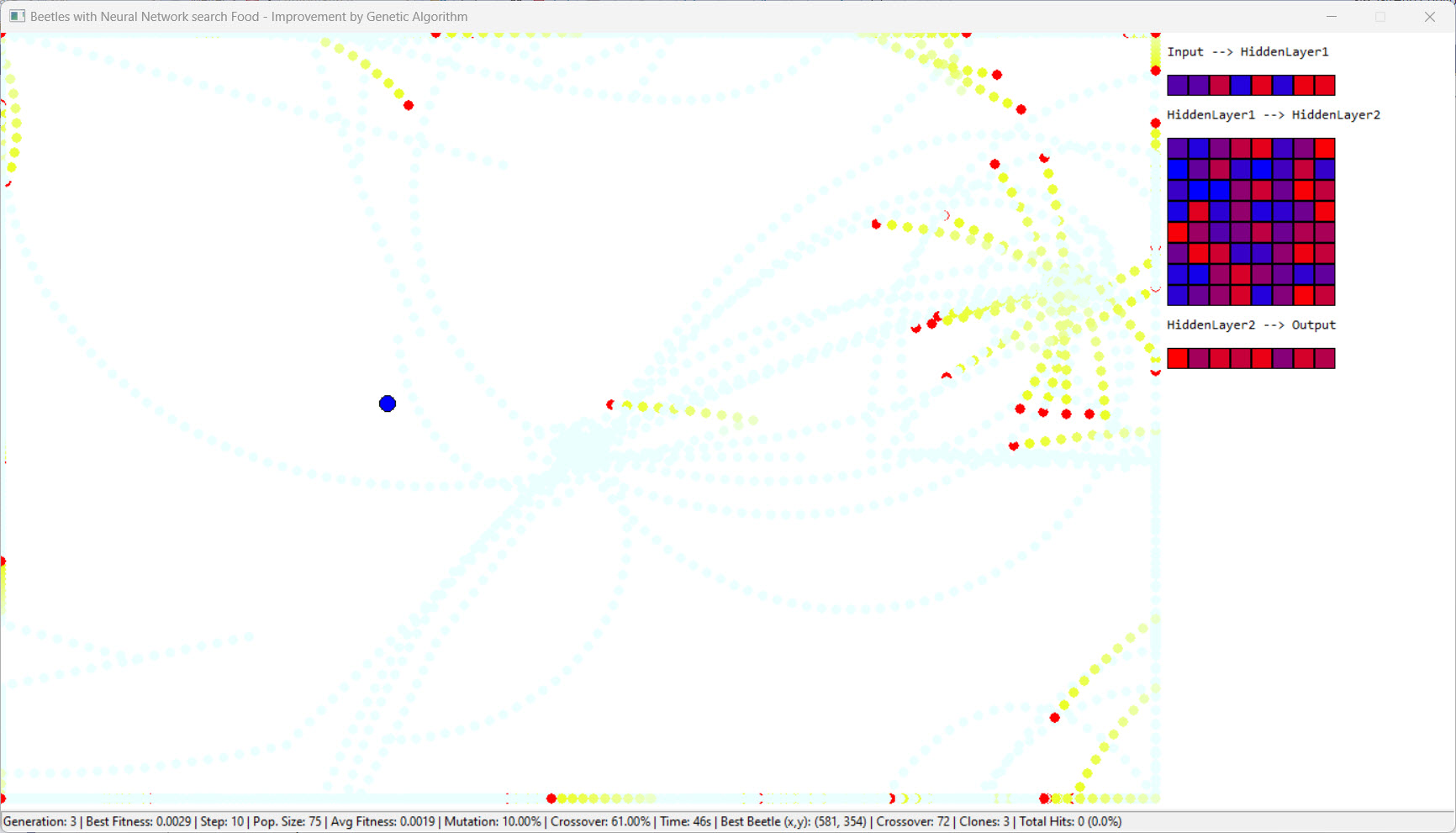
We want to create a concrete experimental playing field here for the topic “Neural Network and Genetic Algorithms”. As an example, we use “beetles” that are looking for “food”.
We use C++ so that we can work in an object-oriented way. For the sake of simplicity, we use WinAPI for the graphical design.
We use a modern IDE (compiler/linker/editor/debugger) as a tool. In this
specific case, we use the free MS Visual Studio 2022.
The Beetle program is designed as an experimental
platform to explore the integration of neural networks with genetic algorithms.
The primary objective is to simulate the behavior of a beetle-like agent in a
two-dimensional environment, allowing for the testing and optimization of neural
network-based decision-making through evolutionary strategies.
Each beetle agent is equipped with a neural network that takes inputs related to its environment and outputs movement commands. The neural network's architecture is defined by parameters such as the number of input and output nodes, hidden layers, and the size of hidden layers.
The program incorporates genetic algorithms to evolve the neural networks over generations. Key genetic operations include:
Crossover: Combines the neural network weights of two parent beetles to create offspring. The program supports different crossover techniques, including uniform crossover, one-point crossover, and two-point crossover.
Mutation: Introduces random changes to the neural network weights of a beetle with a certain probability, enabling the exploration of new potential solutions and preventing premature convergence.
The simulation environment consists of a defined window where beetles can move and search for food. Key features include:
The beetle's movements, trails, and food are graphically represented using GDI (Graphics Device Interface) functions. Different colors and fading effects are used to visually distinguish between current and past positions and actions.
The program includes debugging output for monitoring internal states and actions. In addition, a sound is played when a beetle successfully finds food or a new generation goes in search of food, hopefully enhancing the interactive aspect of the simulation.
The beetle program serves as a foundational framework for experimenting with neural networks and genetic algorithms. By simulating the beetle's behavior and optimizing its decision-making process through evolutionary strategies, researchers and developers can gain insights into the efficacy of different neural network configurations and genetic operations.
This experimental base can be extended and customized for various research purposes, including:
In summary, the beetle program provides a versatile and interactive platform for advancing the understanding and application of neural networks and genetic algorithms in simulated environments. As a side effect, you can practise C++ and graphical programming using WinAPI.
C++ Code:
We start with the neural network. In C++, we use one
header file and one source file:
NeuralNetwork.h:
#pragma once
#include <vector>
class NeuralNetwork
{
public:
/**
* @brief
Constructs a NeuralNetwork object.
*
* @param inputSize Number of input
neurons.
* @param outputSize Number of output neurons.
* @param
numHiddenLayers Number of hidden layers.
* @param hiddenLayerSize Number of
neurons in each hidden layer.
*/
NeuralNetwork(int inputSize, int
outputSize, int numHiddenLayers, int hiddenLayerSize);
/**
* @brief
Performs a feedforward operation through the network.
*
* @param inputs
Vector of input values.
* @return Vector of output values.
*/
std::vector<double> FeedForward(const std::vector<double>& inputs);
/**
* @brief Retrieves the current weights of the network.
*
* @return
Vector of all weights in the network.
*/
std::vector<double> GetWeights()
const;
/**
* @brief Sets the weights of the network.
*
*
@param newWeights Vector of weights to be set.
*/
void SetWeights(const
std::vector<double>& newWeights);
/**
* @brief Sigmoid activation function.
*
* @param x Input value.
* @return Activated value.
*/
double Sigmoid(double
x);
/**
* @brief ReLU
activation function.
*
* @param x Input value.
* @return Activated
value.
*/
double ReLU(double
x);
private:
/**
*
@brief Initializes the weights of the network randomly.
*/
void
InitializeWeights();
std::vector<std::vector<double>> weights;
///<
Vector of weight matrices for each layer.
int
inputSize; ///< Number of input neurons.
int outputSize;
///< Number of output neurons.
int
numHiddenLayers; ///< Number of hidden layers.
int hiddenLayerSize;
///< Number of neurons in each hidden layer.
};
NeuralNetwork.cpp:
#include <random>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <cassert>
#include <sstream>
#include
"NeuralNetwork.h"
#include "DebugOutput.h"
#include "ConstantData.h"
/**
* @brief Constructs a NeuralNetwork object.
*
* @param
inputSize Number of input neurons.
* @param outputSize Number of output
neurons.
* @param numHiddenLayers Number of hidden layers.
* @param
hiddenLayerSize Number of neurons in each hidden layer.
*/
NeuralNetwork::NeuralNetwork(int inputSize, int outputSize, int numHiddenLayers,
int hiddenLayerSize)
: inputSize(inputSize), outputSize(outputSize),
numHiddenLayers(numHiddenLayers), hiddenLayerSize(hiddenLayerSize)
{
InitializeWeights();
// Initializes the weights of the network randomly.
}
/**
* @brief Initializes the weights of the network
randomly.
*/
void
NeuralNetwork::InitializeWeights()
{
std::random_device rd;
std::mt19937 gen(rd());
std::uniform_real_distribution<> dis(-1.0, 1.0);
// Initialize weights for input to first hidden layer
weights.push_back(std::vector<double>(inputSize * hiddenLayerSize));
std::generate(weights.back().begin(), weights.back().end(), [&]() { return
dis(gen); });
// Initialize weights for hidden layers
for (int i = 0;
i < numHiddenLayers - 1; ++i)
{
weights.push_back(std::vector<double>(hiddenLayerSize * hiddenLayerSize));
std::generate(weights.back().begin(), weights.back().end(), [&]() { return
dis(gen); });
}
// Initialize weights for last hidden layer to output
layer
weights.push_back(std::vector<double>(hiddenLayerSize * outputSize));
std::generate(weights.back().begin(), weights.back().end(), [&]() { return
dis(gen); });
}
/**
* @brief Performs a
feedforward operation through the network.
*
* @param inputs Vector of
input values.
* @return Vector of output values.
*/
std::vector<double> NeuralNetwork::FeedForward(const std::vector<double>&
inputs)
{
assert(inputs.size() == inputSize);
std::vector<double>
outputs(hiddenLayerSize, 0.0);
std::vector<double> currentInputs = inputs;
// Compute hidden layers
for (int l = 0; l < numHiddenLayers; ++l)
{
outputs.assign(hiddenLayerSize, 0.0);
for (int j = 0; j <
hiddenLayerSize; ++j)
{
for (int i = 0; i < currentInputs.size(); ++i)
{
outputs[j] += currentInputs[i] * weights[l][j * currentInputs.size() + i];
}
if (RELU_FOR_HIDDEN)
{
outputs[j] = ReLU(outputs[j]);
// ReLU activation function
}
}
currentInputs = outputs;
}
// Compute output layer
outputs.assign(outputSize, 0.0);
for (int
j = 0; j < outputSize; ++j)
{
for (int i = 0; i <
currentInputs.size(); ++i)
{
outputs[j] += currentInputs[i] * weights.back()[j * currentInputs.size() + i];
}
if
(SIGMOID_FOR_OUTPUT)
{
outputs[j] = Sigmoid(outputs[j]) * 600 - 300;
// Scale to range [-300, 300] for
beetle movements
}
}
return outputs;
}
/**
* @brief Retrieves the current weights of the
network.
*
* @return Vector of all weights in the network.
*/
std::vector<double> NeuralNetwork::GetWeights() const
{
// Concatenate all weight matrices into a single vector
std::vector<double> allWeights;
for (const auto&
layerWeights : weights)
{
allWeights.insert(allWeights.end(), layerWeights.begin(), layerWeights.end());
}
return allWeights;
}
/**
* @brief Sets the
weights of the network.
*
* @param newWeights Vector of weights to be
set.
*/
void NeuralNetwork::SetWeights(const std::vector<double>&
newWeights)
{
size_t offset = 0;
for (auto& layerWeights : weights)
{
std::copy(newWeights.begin() + offset, newWeights.begin() + offset +
layerWeights.size(), layerWeights.begin());
offset += layerWeights.size();
}
}
/**
*
@brief Sigmoid activation function.
*
* @param x Input value.
*
@return Activated value.
*/
double NeuralNetwork::Sigmoid(double x)
{
return 1.0 / (1.0 + exp(-x));
}
/**
* @brief ReLU activation
function.
*
* @param x Input value.
* @return Activated value.
*/
double NeuralNetwork::ReLU(double x)
{
return
std::max(0.0, x);
}
Explanation:
Class:
NeuralNetwork
Purpose: The
NeuralNetwork
class represents a simple feedforward neural network with configurable input
size, output size, number of hidden layers, and hidden layer size.
Public Methods
Constructor:
Initializes the network with given input size, output size, number of hidden layers, and hidden layer size.
Calls
InitializeWeights()
to set initial random weights.
FeedForward:
Performs the feedforward process, calculating the output of the network for a given set of inputs.
Supports activation functions: If desired, ReLU for hidden layers and Sigmoid for the output layer.
GetWeights:
Returns a single vector containing all the weights of the network.
SetWeights:
Sets the weights of the network from a given vector.
Sigmoid:
Computes the Sigmoid activation function.
ReLU:
Computes the ReLU activation function.
Private Methods
InitializeWeights:
Randomly initializes the weights for each layer in the network.
The neural network will be the “brain” of the
beetles. We need parameters for our program code to function and for
experimentation.
We summarize these as follows:
ConstantData.h:
#pragma once
constexpr bool TEST_WITHOUT_NN = false;
extern int TotalHitsPerGeneration;
extern int FOOD_X;
extern int
FOOD_Y;
constexpr int POPULATION_SIZE = 75;
constexpr int GENERATION_INTERVAL = 70;
constexpr int WINDOW_WIDTH =
1100;
constexpr int WINDOW_EXTRAWIDTH = 300;
constexpr int WINDOW_HEIGHT =
800;
constexpr int STATUS_HEIGHT = 70;
constexpr int FOOD_SHIFT_X = 500;
constexpr int FOOD_SHIFT_Y =
280;
constexpr int FOOD_SIZE = 8;
constexpr int BEETLE_SIZE = 5;
constexpr int FOOD_HIT = FOOD_SIZE;
constexpr int TRAIL_MAX_LENGTH = 100;
constexpr int TRAIL_COLOR_PARAMETER1 = 235;
constexpr int FADING_FACTOR = 20;
constexpr double SPEED = 15;
constexpr int INPUT_SIZE = 1;
constexpr
int OUTPUT_SIZE = 1;
constexpr int NUM_HIDDEN_LAYERS = 2;
constexpr int
HIDDEN_LAYER_SIZE = 8;
constexpr bool RELU_FOR_HIDDEN = false;
constexpr
bool SIGMOID_FOR_OUTPUT = false;
constexpr int HEATMAP_SIZE = INPUT_SIZE
* HIDDEN_LAYER_SIZE +
NUM_HIDDEN_LAYERS * HIDDEN_LAYER_SIZE *
HIDDEN_LAYER_SIZE +
HIDDEN_LAYER_SIZE * OUTPUT_SIZE;
constexpr int
CELL_SIZE = 20; // Die Größe jeder Zelle in der
Heatmap
constexpr int HEATMAP_DIM_X = HEATMAP_SIZE /
HIDDEN_LAYER_SIZE;
constexpr int HEATMAP_DIM_Y = HIDDEN_LAYER_SIZE;
constexpr double MUTATION_MIN = -0.1;
constexpr double MUTATION_MAX = 0.1;
constexpr int BEST_SELECTOR = 2; // Divisor 2
bedeutet 50% für die Reproduktion
constexpr int CROSSOVER_TYPE = 2;
constexpr bool CLONING_FORBIDDEN = false;
constexpr COLORREF BLUE = RGB(0, 0, 255);
constexpr COLORREF RED =
RGB(255, 0, 0);
constexpr COLORREF GREEN = RGB(0, 255, 0);
constexpr
COLORREF WHITE = RGB(255, 255, 255);
constexpr COLORREF GRAY = RGB(128, 128,
128);
constexpr COLORREF LIGHTGRAY = RGB(211, 211, 211);
constexpr int
STATUS_UPDATE_INTERVAL1 = 300;
constexpr int STATUS_UPDATE_INTERVAL2 = 3000;
constexpr int SLEEP_TIME = 0;
The ideal way to experiment with this is to change
parameters in this header file and then start the debugging process.
We use
the following function to generate our own debugging outputs:
DebugOutput.h:
#pragma once
#include <string>
#define NOMINMAX
#include <windows.h>
void DebugOutput(const std::string& message);
DebugOutput.cpp:
#include <windows.h>
#include <string>
#include <sstream>
#include "DebugOutput.h"
void DebugOutput(const std::string& message)
{
OutputDebugStringA((message + "\n").c_str());
}
A brain alone can only accomplish abstract things. In
order for us to see and experience something, we use our neural network in
"beetles" that are supposed to search for "food".
To do this, we create our
Beetle class:
The Beetle class simulates the behavior of a
beetle in a 2D environment using a neural network to determine its movements.
Each beetle has unique properties and capabilities, such as detecting food
by smell, moving towards
food, drawing itself on the screen, leaving a trail, performing crossover and
mutation operations for genetic algorithms, and maintaining a trail of its past
positions.
Beetle.h:
#pragma once
#include
"NeuralNetwork.h"
#define NOMINMAX
#include "windows.h"
struct
TrailSegment
{
int x;
int y;
int age;
};
class Beetle
{
public:
Beetle();
void
Move();
void Draw(HDC hdc);
Beetle
Crossover(const Beetle& other, double crossoverRate, int type) const;
void
Mutate(double mutationRate);
NeuralNetwork& GetNeuralNetwork();
const
NeuralNetwork& GetNeuralNetwork() const;
// Get and Set
functions
int GetID()
const { return id; }
int GetX()
const { return x; }
int GetY() const { return y; }
void
SetCurrentGeneration(bool current) { isCurrentGeneration = current; }
void
SetFoodX(int x) { foodX = x; }
void SetFoodY(int y) { foodY = y; }
const
int GetFoodX() { return foodX; };
const int GetFoodY() { return foodY; };
bool IsFoodFound() const { return foodFound; }
void SetFoodFound(bool value)
{ foodFound = value; }
private:
NeuralNetwork neuralNetwork;
static
int nextId; // Statische Variable zur Generierung
eindeutiger IDs
int id;
int x;
int y;
int foodX;
int foodY;
bool foodFound;
static bool foodMoved;
std::vector<TrailSegment> trail;
bool isCurrentGeneration;
};
Beetle.cpp:
#include "Beetle.h"
#include
<random>
#include <string>
#include <sstream>
#include <cassert>
#include <cmath>
#include "DebugOutput.h"
#include "ConstantData.h"
// Zum Abspielen von Sound
#include <mmsystem.h>
#pragma comment(lib, "winmm.lib")
int Beetle::nextId = 0;
// Initialisierung der statischen Variable
// Initializes a beetle with random starting coordinates
within the window bounds and sets default values for food location, generation
status, and ID
Beetle::Beetle() : neuralNetwork(INPUT_SIZE, OUTPUT_SIZE,
NUM_HIDDEN_LAYERS, HIDDEN_LAYER_SIZE)
{
// Uses a
random device and Mersenne Twister generator to assign random initial positions
to the beetle within the specified window dimensions
std::random_device rd;
std::mt19937 gen(rd());
std::uniform_int_distribution<> disX(0, WINDOW_WIDTH - 1);
std::uniform_int_distribution<> disY(0, WINDOW_HEIGHT - 1 - STATUS_HEIGHT);
x = disX(gen);
y = disY(gen);
foodX = FOOD_X;
foodY = FOOD_Y;
foodFound = false;
isCurrentGeneration = false;
id = nextId++;
}
// Asserts correct input size, processes inputs to
compute movement deltas, updates position,
// checks for food detection, updates
the trail, and ensures the trail length does not exceed the maximum
void
Beetle::Move()
{
// Berechnung der Differenz
zwischen der aktuellen Position und der Position des Futters
double
deltaFoodX = GetFoodX() - x;
double deltaFoodY = GetFoodY() - y;
// Berechne Winkel zum Futter
double
angleToFood = atan2(deltaFoodY, deltaFoodX);
// Normalisiere den Winkel im Bereich [0, 1]
double normalizedAngle =
(angleToFood + M_PI) / (2 * M_PI);
double moveAngle = 0;
// Bewegungsrichtung
if
(TEST_WITHOUT_NN) // sollte 100% Hits ergeben
{
moveAngle = normalizedAngle * 2 * M_PI - M_PI;
// Normalisiere den Winkel im Bereich [-PI, PI]
}
else // NN wird verwendet
{
// Der normalisierte Winkel ist der Input für
das NN
std::vector<double> inputs;
inputs.push_back(normalizedAngle);
//
Der Output des NN bestimmt die Bewegungsrichtung
std::vector<double> outputs = neuralNetwork.FeedForward(inputs);
moveAngle = outputs[0] * 2 * M_PI - M_PI; //
Normalisiere den Winkel im Bereich [-PI, PI]
}
// Ermittle deltaX und deltaY aus der
Bewegungsrichtung
double deltaX = cos(moveAngle) * SPEED;
double
deltaY = sin(moveAngle) * SPEED;
// Updates the beetle's position while ensuring it
stays within window bounds
double newX = x + deltaX * SPEED;
if (newX >=
WINDOW_WIDTH) newX = WINDOW_WIDTH - 1;
if (newX < 0) newX = 0;
double newY
= y + deltaY * SPEED;
if (newY >= WINDOW_HEIGHT - STATUS_HEIGHT) newY =
WINDOW_HEIGHT - STATUS_HEIGHT - 1;
if (newY < 0) newY = 0;
x =
static_cast<int>(newX);
y = static_cast<int>(newY);
// Checks if the
beetle has found food, plays a sound if so, updates the trail, and manages trail
length
if (((x <= (foodX + FOOD_HIT) && x >= (foodX - FOOD_HIT))) && ((y <=
(foodY + FOOD_HIT) && y >= (foodY - FOOD_HIT))) && !foodFound)
{
foodFound = true;
if (!::PlaySound(TEXT("food_sound.wav"),
NULL, SND_FILENAME | SND_ASYNC))
{
std::ostringstream oss;
oss <<
"\n>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>Error playing sound";
DebugOutput(oss.str());
}
}
TrailSegment
segment = { x, y, 0 };
trail.push_back(segment);
if (!trail.empty() &&
(trail.size() > TRAIL_MAX_LENGTH))
{
TrailSegment
oldSegment = trail.front();
trail.erase(trail.begin());
}
for (auto& segment : trail)
{
segment.age++;
}
}
// Draws the beetle, its trail, and the food on the
screen using GDI functions
void Beetle::Draw(HDC hdc)
{
// Define
colors
COLORREF foodColor = BLUE;
COLORREF OldFoodColor = GRAY;
COLORREF currentBeetleColor = RED;
COLORREF oldBeetleColor = LIGHTGRAY;
// Draw food
HBRUSH hFoodBrush =
CreateSolidBrush(foodColor);
HBRUSH hOldFoodBrush =
CreateSolidBrush(OldFoodColor);
if (isCurrentGeneration)
{
SelectObject(hdc, hFoodBrush);
}
else
{
SelectObject(hdc,
hOldFoodBrush);
}
// Draws the food as a filled circle
Ellipse(hdc,
GetFoodX() - FOOD_SIZE, GetFoodY() - FOOD_SIZE, GetFoodX() + FOOD_SIZE,
GetFoodY() + FOOD_SIZE);
DeleteObject(hFoodBrush);
DeleteObject(hOldFoodBrush);
// Trail Drawing: Draws each segment of the
trail with varying transparency based on age
for (auto& segment : trail)
{
int alpha = 0 + (segment.age * FADING_FACTOR);
if (alpha
> 255) alpha = 255;
int red = TRAIL_COLOR_PARAMETER1;
int green = 255;
int blue = (255 * alpha) / 255;
COLORREF trailColor = RGB(red, green, blue);
HBRUSH
hTrailBrush = CreateSolidBrush(trailColor);
HBRUSH
hOldTrailBrush = (HBRUSH)SelectObject(hdc, hTrailBrush);
HPEN hTrailPen = CreatePen(PS_SOLID, 1, trailColor);
HPEN
hOldPen = (HPEN)SelectObject(hdc, hTrailPen);
Ellipse(hdc, segment.x - BEETLE_SIZE, segment.y - BEETLE_SIZE, segment.x +
BEETLE_SIZE, segment.y + BEETLE_SIZE);
SelectObject(hdc, hOldTrailBrush);
SelectObject(hdc,
hOldPen);
DeleteObject(hTrailBrush);
DeleteObject(hTrailPen);
}
// Draws the beetle as a filled circle
HPEN hCurrentBeetlePen = CreatePen(PS_SOLID, 1, currentBeetleColor);
HBRUSH
hCurrentBeetleBrush = CreateSolidBrush(currentBeetleColor);
HPEN
hOldBeetlePen = CreatePen(PS_SOLID, 1, oldBeetleColor);
HBRUSH
hOldBeetleBrush = CreateSolidBrush(oldBeetleColor);
if
(!isCurrentGeneration)
{
HPEN hOldPen =
(HPEN)SelectObject(hdc, hOldBeetlePen);
HBRUSH hOldBrush =
(HBRUSH)SelectObject(hdc, hOldBeetleBrush);
// Käfer zeichnen (als gefüllter Kreis)
Ellipse(hdc, x - BEETLE_SIZE, y - BEETLE_SIZE, x + BEETLE_SIZE, y +
BEETLE_SIZE);
SelectObject(hdc, hOldPen);
SelectObject(hdc, hOldBrush);
}
else
{
HPEN
hOldPen = (HPEN)SelectObject(hdc, hCurrentBeetlePen);
HBRUSH hOldBrush = (HBRUSH)SelectObject(hdc, hCurrentBeetleBrush);
// Käfer zeichnen (als gefüllter Kreis)
Ellipse(hdc, x - BEETLE_SIZE, y - BEETLE_SIZE, x + BEETLE_SIZE, y +
BEETLE_SIZE);
SelectObject(hdc, hOldPen);
SelectObject(hdc, hOldBrush);
}
DeleteObject(hCurrentBeetlePen);
DeleteObject(hCurrentBeetleBrush);
DeleteObject(hOldBeetlePen);
DeleteObject(hOldBeetleBrush);
}
// Produces an offspring beetle by
combining the weights of two parent beetles according to the specified crossover
type (uniform, one-point, or two-point)
Beetle Beetle::Crossover(const
Beetle& other, double crossoverRate, int type) const
{
Beetle offspring;
std::random_device rd;
std::mt19937 gen(rd());
std::uniform_real_distribution<> dis(0.0, 1.0);
std::uniform_int_distribution<> pointDist(0,
static_cast<int>(this->GetNeuralNetwork().GetWeights().size() - 1));
std::vector<double> offspringWeights =
offspring.GetNeuralNetwork().GetWeights();
const std::vector<double>&
thisWeights = this->GetNeuralNetwork().GetWeights();
const
std::vector<double>& otherWeights = other.GetNeuralNetwork().GetWeights();
if (thisWeights.size() != otherWeights.size())
{
throw std::runtime_error("Crossover: Weight vectors must be of the same size");
}
size_t crossoverPoint = 0;
size_t point1 = 0, point2 = 0;
switch (type)
{
case 0: // Uniforme Crossover
// A random value
(dis(gen)) decides for each weight,
// whether the weight is passed on from
the current beetle (thisWeights[i])
// or from the other parent
(otherWeights[i]) to the offspring.
// This is based on the crossoverRate.
for (size_t i = 0; i < thisWeights.size(); ++i)
{
offspringWeights[i] = (dis(gen) < crossoverRate) ? thisWeights[i] :
otherWeights[i];
}
break;
case 1: // One-Point Crossover
// A
single random crossover point is selected (crossoverPoint),
// where the
pointDist manifold is used to determine the position of the crossover point.
// All weights before this point come from the current beetle (thisWeights),
// and all weights from this point onwards come from the other parent
(otherWeights).
crossoverPoint = pointDist(gen);
for (size_t i = 0; i <
thisWeights.size(); ++i)
{
offspringWeights[i] = (i <
crossoverPoint) ? thisWeights[i] : otherWeights[i];
}
break;
case
2: // Two-Point Crossover
// Two random intersection points are selected
(point1 and point2),
// where the pointDist distributor is used to determine
the position of the intersection points.
// If the first point is larger
than the second, the points are swapped,
// to ensure that the first point
is less than or equal to the second (std::swap).
// Weights before the first
point and after the second point come from the current beetle (thisWeights),
// while the weights between the points come from the other parent
(otherWeights).
point1 = pointDist(gen); // Der pointDist-Verteiler:
zufälliger erster Kreuzungspunkt
point2 = pointDist(gen); // Der
pointDist-Verteiler: zufälliger zweiter Kreuzungspunkt
if (point1 >
point2) std::swap(point1, point2); // The std::swap function ensures
// that
the first intersection point is less than or equal to the second,
// which
simplifies the implementation of the two-point intersection.
for (size_t
i = 0; i < thisWeights.size(); ++i)
{
offspringWeights[i] = (i < point1 || i > point2) ? thisWeights[i] :
otherWeights[i];
}
break;
default:
throw
std::invalid_argument("Invalid crossover type");
}
offspring.GetNeuralNetwork().SetWeights(offspringWeights);
offspring.foodFound = false;
return offspring;
}
// Randomly alters
the weights of the beetle's neural network based on the mutation rate
void
Beetle::Mutate(double mutationRate)
{
std::random_device rd;
std::mt19937 gen(rd());
std::uniform_real_distribution<> dis(0.0, 1.0);
std::normal_distribution<> mutationDist(0.0, 1.0);
std::vector<double>
weights = neuralNetwork.GetWeights();
// Each weight has a probability (mutationRate)
of being altered by a value drawn from a normal distribution
// If the random
number is smaller than the mutationRate,
// the weight is changed by a value
mutationDist(gen),
// which comes from the normal distribution.
// This
combination of a uniform distribution for decision making
// and a normal
distribution to determine the mutation size is a common approach in genetic
algorithms and evolutionary strategies,
// as it strikes a good balance
between exploration (through mutations)
// and exploitation (by crossing).
for (auto& weight : weights)
{
if (dis(gen) <
mutationRate)
{
weight += mutationDist(gen);
}
}
neuralNetwork.SetWeights(weights);
foodFound = false;
}
// Provides
access to the beetle's neural network for both modification and read-only
purposes
NeuralNetwork& Beetle::GetNeuralNetwork()
{
return neuralNetwork;
}
const NeuralNetwork&
Beetle::GetNeuralNetwork() const
{
return
neuralNetwork;
}
The presentation and movement of the beetles
can certainly be optimized even further. However, this is already sufficient as
an experimental base.
Now comes the genetic algorithm, the core of our
optimization from generation to generation. We use crossover and mutation to
produce beetles with hopefully increased fitness.
GeneticAlgorithm.h:
#pragma once
#include <vector>
#include "Beetle.h"
class GeneticAlgorithm
{
public:
std::pair<std::vector<Beetle>,
std::pair<int, int>> NextGeneration(const std::vector<Beetle>&
currentGeneration, double mutationRate, double crossoverRate);
double
CalculateAverageFitness(const std::vector<Beetle>& beetles);
double
GetMutationRate(double previousBestFitness, double currentBestFitness);
double GetCrossoverRate(double previousAverageFitness, double
currentAverageFitness);
};
GeneticAlgorithm.cpp:
#define NOMINMAX
#include
"GeneticAlgorithm.h"
#include <algorithm>
#include <random>
#include
<cassert>
#include <sstream>
#include "DebugOutput.h"
#include
"Beetle.h"
#include "NeuralNetwork.h"
#include "ConstantData.h"
double GeneticAlgorithm::CalculateAverageFitness(const std::vector<Beetle>&
beetles)
{
double totalFitness = 0.0;
for (const auto& beetle :
beetles)
{
double distance = sqrt(pow(beetle.GetX() -
FOOD_X, 2) + pow(beetle.GetY() - FOOD_Y, 2));
double
fitness = 1.0 / (distance + 1);
// Avoid division by zero
totalFitness += fitness;
}
return totalFitness / beetles.size();
}
double GeneticAlgorithm::GetMutationRate(double previousBestFitness, double
currentBestFitness)
{
static double mutationRate = 0.01;
// Start value
double fitnessImprovement = currentBestFitness - previousBestFitness;
if
(fitnessImprovement < 0.01)
{
mutationRate =
std::min(0.1, mutationRate + 0.005);
// Increases the mutation rate, up to a
maximum of 10%
}
else
{
mutationRate =
std::max(0.001, mutationRate - 0.001);
// Reduces the mutation rate, down to a
minimum of 0.1%
}
return mutationRate;
}
double
GeneticAlgorithm::GetCrossoverRate(double previousAverageFitness, double
currentAverageFitness)
{
static double crossoverRate = 0.7;
// Start value
double fitnessImprovement = currentAverageFitness - previousAverageFitness;
if (fitnessImprovement < 0.01)
{
crossoverRate =
std::min(0.9, crossoverRate + 0.01);
// Increases the crossing rate, up to a
maximum of 90%
}
else
{
crossoverRate =
std::max(0.5, crossoverRate - 0.01);
// Reduces the crossover rate, down to a
minimum of 50%
}
return crossoverRate;
}
double
CalculateFitness(const Beetle& beetle)
{
double distance =
sqrt(pow(beetle.GetX() - FOOD_X, 2) + pow(beetle.GetY() - FOOD_Y, 2));
return
1.0 / (distance + 1); // Avoid division by zero
}
std::pair<std::vector<Beetle>, std::pair<int, int>>
GeneticAlgorithm::NextGeneration(const std::vector<Beetle>& currentGeneration,
double mutationRate, double crossoverRate)
{
std::vector<Beetle>
newGeneration;
newGeneration.reserve(currentGeneration.size());
int
crossoverCount = 0;
int cloneCount = 0;
// Fitness calculation
std::vector<std::pair<Beetle, double>> fitnessScores;
for (const auto& beetle
: currentGeneration)
{
double fitness =
CalculateFitness(beetle);
fitnessScores.push_back({
beetle, fitness });
}
// Sort by fitness
std::sort(fitnessScores.begin(), fitnessScores.end(), [](const auto& a, const
auto& b){return a.second > b.second;});
// Selection: Choose the best
beetles for reproduction
int numParents =
static_cast<int>(currentGeneration.size() / BEST_SELECTOR);
numParents =
std::max(1, numParents); // At least one parent
std::vector<Beetle> parents;
for (int i = 0; i < numParents; ++i)
{
parents.push_back(fitnessScores[i].first);
}
// Crossover and mutation
lead to a new generation
std::random_device rd;
std::mt19937 gen(rd());
std::uniform_int_distribution<> dist(0, numParents - 1);
while
(newGeneration.size() < currentGeneration.size()) {
Beetle parent1 =
parents[dist(gen)];
Beetle parent2 = parents[dist(gen)];
if
(CLONING_FORBIDDEN)
{
// Avoid "crossing" the same
parent
while (parent1.GetID() == parent2.GetID())
{
parent2 = parents[dist(gen)];
}
}
Beetle offspring;
if (parent1.GetID() == parent2.GetID())
{
offspring = parent1; // Cloning
cloneCount++;
}
else
{
offspring = parent1.Crossover(parent2,
crossoverRate, CROSSOVER_TYPE);
// Crossover
crossoverCount++;
}
offspring.Mutate(mutationRate);
offspring.SetFoodFound(false);
newGeneration.push_back(offspring);
}
return { newGeneration, { crossoverCount, cloneCount } };
}
Now we
need a main program that displays the events graphically. We choose the classic
WinAPI programming for this, as we can pack everything into one file.
WinAPI
programming has become much easier with the support of AI. You save yourself a
lot of searching for function definitions, headers and libraries.
Main.cpp:
#define NOMINMAX
#include
<windows.h>
#include <limits>
#include <cassert>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <random>
#include <string>
#include
<sstream>
#include <cmath>
#include <chrono>
#include <commctrl.h>
//
For the status bar
#include "Beetle.h"
#include "GeneticAlgorithm.h"
#include "DebugOutput.h"
#include "ConstantData.h"
#include <mmsystem.h>
// For PlaySound
#pragma comment(lib, "winmm.lib")
// For PlaySound
#pragma comment(lib, "comctl32.lib")
// For the status bar
#pragma
comment(lib, "Msimg32.lib") //
library used by Windows to draw transparent images and gradients
std::ostringstream oss; //Debug
int FOOD_X = WINDOW_WIDTH / 2;
int
FOOD_Y = WINDOW_HEIGHT / 2;
int generationStep = 0;
NeuralNetwork bestNN
(INPUT_SIZE, OUTPUT_SIZE, NUM_HIDDEN_LAYERS, HIDDEN_LAYER_SIZE);
int
currentGeneration = 0;
double bestFitness = 0.0;
double
previousBestFitness = 0.0;
double previousAverageFitness = 0.0;
std::vector<Beetle> currentBeetles(POPULATION_SIZE);
std::vector<Beetle>
previousBeetles;
std::pair<int, int> counts;
HWND hStatus;
GeneticAlgorithm geneticAlgorithm; // Instance of GeneticAlgorithm
void
ClearScreen(HWND hwnd)
{
// Receive
handle of the device context of the window
HDC hdc = GetDC(hwnd);
//
Determine the client area of the window
RECT clientRect;
GetClientRect(hwnd, &clientRect);
// Fill the client area with white
HBRUSH hWhiteBrush = CreateSolidBrush(WHITE);
FillRect(hdc, &clientRect,
hWhiteBrush);
DeleteObject(hWhiteBrush);
ReleaseDC(hwnd, hdc);
}
// This sound should be played
when switching to a new generation
void PlayGenerationSound()
{
::PlaySound(TEXT("generation_sound.wav"), NULL, SND_FILENAME | SND_ASYNC);
}
static void UpdateStatusBar(HWND
hwnd, int generation, double bestFitness, int step, size_t populationSize,
double avgFitness, double mutationRate, double crossoverRate, size_t
elapsedTime, int bestBeetleX, int bestBeetleY, int crossoverCount, int
cloneCount, int TotalHitsPerGeneration)
{
wchar_t statusText[512];
swprintf_s(statusText,
L"Generation: %d | Best Fitness: %.4f | Step: %d |
Pop. Size: %zu | Avg Fitness: %.4f | Mutation: %.2f%% | Crossover: %.2f%% |
Time: %zus | Best Beetle (x,y): (%d, %d) | Crossover: %d | Clones: %d | Total
Hits: %d (%.1f%%)",
generation+1, bestFitness, step+1, populationSize,
avgFitness, mutationRate * 100, crossoverRate * 100, elapsedTime, bestBeetleX,
bestBeetleY, crossoverCount, cloneCount, TotalHitsPerGeneration,
(100.0*TotalHitsPerGeneration)/POPULATION_SIZE);
SendMessage(hwnd,
SB_SETTEXT, 0, (LPARAM)statusText);
// Only invalidate
the status bar area
RECT rect;
SendMessage(hwnd, SB_GETRECT, 0,
(LPARAM)&rect);
InvalidateRect(hwnd, &rect, TRUE);
}
size_t GetElapsedTimeInSeconds()
{
static auto startTime =
std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
auto elapsed =
std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::seconds>(std::chrono::steady_clock::now()
- startTime);
return elapsed.count();
}
int GetBestBeetleX(const std::vector<Beetle>& beetles)
{
double
bestFitness = 0.0;
int bestX = 0;
for (const auto& beetle : beetles)
{
double distance = sqrt(pow(beetle.GetX() - FOOD_X, 2) + pow(beetle.GetY() -
FOOD_Y, 2));
double fitness = 1.0 / (distance + 1);
if (fitness > bestFitness)
{
bestFitness = fitness;
bestX =
beetle.GetX();
}
}
return bestX;
}
int GetBestBeetleY(const std::vector<Beetle>& beetles)
{
double
bestFitness = 0.0;
int bestY = 0;
for (const auto& beetle : beetles)
{
double distance = sqrt(pow(beetle.GetX() - FOOD_X, 2) + pow(beetle.GetY() -
FOOD_Y, 2));
double fitness = 1.0 / (distance + 1);
if (fitness > bestFitness)
{
bestFitness = fitness;
bestY =
beetle.GetY();
}
}
return bestY;
}
// The weights between the neurons should be displayed graphically as a heat
map
void DrawWeightHeatmap(HDC hdc, const std::vector<double>& weights, int
x, int y, int cellSize)
{
size_t
num_weights = weights.size();
int input_to_hidden_size = INPUT_SIZE *
HIDDEN_LAYER_SIZE;
int hidden_to_hidden_size = HIDDEN_LAYER_SIZE *
HIDDEN_LAYER_SIZE;
int hidden_to_output_size = HIDDEN_LAYER_SIZE *
OUTPUT_SIZE;
double min_weight = std::numeric_limits<double>::max();
double max_weight = std::numeric_limits<double>::lowest();
// Calculation
of min_weight and max_weight
for (const double& weight : weights)
{
if
(weight < min_weight) min_weight = weight;
if (weight > max_weight)
max_weight = weight;
}
// Prevents
division by zero if min_weight == max_weight
if (max_weight == min_weight)
{
max_weight = min_weight + 1.0;
}
// Setting the font
HFONT hFont = CreateFont(cellSize - 5, 0, 0, 0,
FW_NORMAL, FALSE, FALSE, FALSE, DEFAULT_CHARSET,
OUT_DEFAULT_PRECIS,
CLIP_DEFAULT_PRECIS, DEFAULT_QUALITY,
FIXED_PITCH | FF_MODERN, L"Consolas");
HFONT hOldFont = (HFONT)SelectObject(hdc, hFont);
auto draw_rectangle =
[&](int row, int col, int color_intensity)
{
COLORREF color = RGB(color_intensity, 0, 255 - color_intensity);
HBRUSH brush
= CreateSolidBrush(color);
HBRUSH oldBrush = (HBRUSH)SelectObject(hdc,
brush);
Rectangle(hdc, x + col * cellSize, y + row * cellSize, x + (col +
1) * cellSize, y + (row + 1) * cellSize);
SelectObject(hdc, oldBrush);
DeleteObject(brush);
};
auto draw_text = [&](const std::string& text,
int row_offset)
{
TextOutA(hdc, x, y +
row_offset * cellSize - cellSize / 2, text.c_str(),
static_cast<int>(text.length()));
};
int row = 0;
int col = 0;
// Drawing the weights between input and first hidden layer
++row;//
Client area in the upper section covered by caption
draw_text("Input -->
HiddenLayer1", row);
++row;
for (int i = 0; i < input_to_hidden_size; ++i)
{
double weight = weights[i];
int color_intensity = static_cast<int>((weight - min_weight) / (max_weight -
min_weight) * 255);
draw_rectangle(row, col,
color_intensity);
if (++col >= HIDDEN_LAYER_SIZE)
{
col = 0;
++row;
}
}
// Blank line between the layers
++row;
// Drawing the weights
between the hidden layers
for (int l = 0; l < (NUM_HIDDEN_LAYERS-1); ++l) {
std::ostringstream oss;
oss << "HiddenLayer" << l + 1 << " --> HiddenLayer"
<< l + 2;
draw_text(oss.str(), row);
++row;
for (int i = 0; i <
hidden_to_hidden_size; ++i)
{
int index =
input_to_hidden_size + l * hidden_to_hidden_size + i;
double weight = weights[index];
int color_intensity =
static_cast<int>((weight - min_weight) / (max_weight - min_weight) * 255);
draw_rectangle(row, col, color_intensity);
if (++col
>= HIDDEN_LAYER_SIZE)
{
col = 0;
++row;
}
}
//
Blank line between the layers
++row;
}
// Drawing the weights between the last hidden layer and the output layer
std::ostringstream oss;
oss << "HiddenLayer" << NUM_HIDDEN_LAYERS << " -->
Output";
draw_text(oss.str(), row);
++row;
for (int i = 0; i <
hidden_to_output_size; ++i)
{
int index =
input_to_hidden_size + (NUM_HIDDEN_LAYERS-1) * hidden_to_hidden_size + i;
double weight = weights[index];
int color_intensity =
static_cast<int>((weight - min_weight) / (max_weight - min_weight) * 255);
draw_rectangle(row, col, color_intensity);
if (++col
>= HIDDEN_LAYER_SIZE)
{
col = 0;
++row;
}
}
// Restore the original font
SelectObject(hdc, hOldFont);
DeleteObject(hFont);
}
// Window
procedure
LRESULT CALLBACK WindowProc(HWND hwnd, UINT uMsg, WPARAM wParam,
LPARAM lParam)
{
switch (uMsg)
{
case WM_DESTROY:
PostQuitMessage(0);
return 0;
case WM_PAINT:
{
PAINTSTRUCT ps;
HDC hdc = BeginPaint(hwnd, &ps);
// Creating a compatible
DC and bitmap
HDC hdcMem = CreateCompatibleDC(hdc);
HBITMAP hbmMem =
CreateCompatibleBitmap(hdc, WINDOW_WIDTH + WINDOW_EXTRAWIDTH, WINDOW_HEIGHT);
HGDIOBJ hOld = SelectObject(hdcMem, hbmMem);
// Erase background
HBRUSH hbrBkGnd = CreateSolidBrush(RGB(255, 255, 255)); // White background
FillRect(hdcMem, &ps.rcPaint, hbrBkGnd);
DeleteObject(hbrBkGnd);
//
Visualize weights of the best NN as a heat map
std::vector<double> weights =
bestNN.GetWeights();
DrawWeightHeatmap(hdcMem, weights, WINDOW_WIDTH+10, 0,
CELL_SIZE);
// Draw previous generation in gray
for (auto& beetle :
previousBeetles)
{
beetle.SetCurrentGeneration(false);
beetle.Draw(hdcMem);
}
// Draw
current generation in red
for (auto& beetle : currentBeetles)
{
beetle.SetCurrentGeneration(true);
beetle.Draw(hdcMem);
}
// Copy the memory DC to the screen
DC
BitBlt(hdc, 0, 0, WINDOW_WIDTH + WINDOW_EXTRAWIDTH, WINDOW_HEIGHT, hdcMem,
0, 0, SRCCOPY);
SelectObject(hdcMem, hOld);
DeleteObject(hbmMem);
DeleteDC(hdcMem);
EndPaint(hwnd, &ps);
return 0;
}
case WM_TIMER:
{
UINT_PTR timerID =
(UINT_PTR)wParam;
switch (timerID)
{
case 1:
// Refresh status bar
UpdateStatusBar(hStatus, currentGeneration, bestFitness, generationStep,
currentBeetles.size(),
geneticAlgorithm.CalculateAverageFitness(currentBeetles),
geneticAlgorithm.GetMutationRate(previousBestFitness, bestFitness),
geneticAlgorithm.GetCrossoverRate(previousAverageFitness,
geneticAlgorithm.CalculateAverageFitness(currentBeetles)),
GetElapsedTimeInSeconds(), GetBestBeetleX(currentBeetles),
GetBestBeetleY(currentBeetles), counts.first, counts.second,
TotalHitsPerGeneration);
// Movement
logic for the beetles
for (auto& beetle : currentBeetles)
{
beetle.Move();
}
// Determine generation progress and update generations
if
(++generationStep >= GENERATION_INTERVAL)
{
oss << "\ncurrentGeneration: " << currentGeneration
<< " generationStep: " <<
generationStep;
DebugOutput(oss.str());
previousBestFitness =
bestFitness;
previousAverageFitness =
geneticAlgorithm.CalculateAverageFitness(previousBeetles);
generationStep =
0;
currentGeneration++;
TotalHitsPerGeneration = 0;
// Set all beetles in the current generation
to false before they become the old generation
for (auto& beetle :
currentBeetles)
{
beetle.SetCurrentGeneration(false);
}
// Save the current generation in
previousBeetles
previousBeetles = currentBeetles;
oss << "\nbeetle
size old: " << previousBeetles.size();
DebugOutput(oss.str());
// New
position for the food
std::random_device rd;
std::mt19937 gen(rd());
std::uniform_int_distribution<> disX(WINDOW_WIDTH / 2 - FOOD_SHIFT_X,
WINDOW_WIDTH / 2 + FOOD_SHIFT_X); // Range for x-coordinate of the chuck
std::uniform_int_distribution<> disY(WINDOW_HEIGHT / 2 - FOOD_SHIFT_Y,
WINDOW_HEIGHT / 2 + FOOD_SHIFT_Y); // Range for y-coordinate of the chuck
// Random position for the food in the defined area
FOOD_X = disX(gen);
FOOD_Y = disY(gen);
// Creating a new generation
auto result =
geneticAlgorithm.NextGeneration(previousBeetles,
geneticAlgorithm.GetMutationRate(previousBestFitness, bestFitness),
geneticAlgorithm.GetCrossoverRate(previousAverageFitness,
geneticAlgorithm.CalculateAverageFitness(previousBeetles)));
std::vector<Beetle> newGeneration = result.first;
counts = result.second;
oss << "\nbeetle size new: " << currentBeetles.size();
DebugOutput(oss.str());
// Set all beetles in the new generation to true
for (auto& beetle : currentBeetles)
{
beetle.SetCurrentGeneration(true);
beetle.SetFoodX(FOOD_X);
beetle.SetFoodY(FOOD_Y);
beetle.SetFoodFound(false);
}
::PlayGenerationSound(); // Play sound when a new generation appears
//
Calculate the best fitness of the new generation
bestFitness = 0.0;
for
(const auto& beetle : currentBeetles)
{
double distance = sqrt(pow(beetle.GetX() - FOOD_X, 2) + pow(beetle.GetY() -
FOOD_Y, 2));
double fitness = 1.0 / (distance + 1); //
Vermeiden von Division durch Null
if (fitness >
bestFitness)
{
bestFitness = fitness;
bestNN =
beetle.GetNeuralNetwork();
}
}
// Drawing the beetles after generation
change
InvalidateRect(hwnd, NULL, TRUE);
}
break;
case 2:
ClearScreen(hwnd); //Remove artifacts
break;
default:
// Handler for unknown timer IDs
break;
}
}
// Refresh window
InvalidateRect(hwnd, NULL, TRUE);
return 0;
}
return DefWindowProc(hwnd, uMsg, wParam, lParam);
}
// Point of entry
int WINAPI wWinMain(HINSTANCE hInstance, HINSTANCE
hPrevInstance, LPWSTR lpCmdLine, int nCmdShow) {
INITCOMMONCONTROLSEX icex;
// Common Controls
icex.dwSize =
sizeof(INITCOMMONCONTROLSEX);
icex.dwICC = ICC_WIN95_CLASSES;
// Correct
initialization of the Common Controls
InitCommonControlsEx(&icex);
constexpr wchar_t CLASS_NAME[] = L"BeetleWindowClass";
WNDCLASS wc = {};
wc.lpfnWndProc = WindowProc;
wc.hInstance = hInstance;
wc.lpszClassName =
CLASS_NAME;
wc.hCursor = LoadCursor(NULL, IDC_ARROW);
RegisterClass(&wc);
HWND hwnd = CreateWindowEx(
0,
CLASS_NAME,
L"Beetles with Neural Network search Food - Improvement by Genetic Algorithm",
WS_OVERLAPPED | WS_CAPTION | WS_SYSMENU | WS_MINIMIZEBOX,
CW_USEDEFAULT,
CW_USEDEFAULT, WINDOW_WIDTH + WINDOW_EXTRAWIDTH, WINDOW_HEIGHT,
NULL,
NULL,
hInstance,
NULL
);
if (hwnd == NULL) {
return 0;
}
// Creating the status bar
hStatus
= CreateWindowEx(
0, STATUSCLASSNAME, NULL,
WS_CHILD | WS_VISIBLE,
0,
0, 0, 0,
hwnd, (HMENU)1, GetModuleHandle(NULL), NULL
);
ShowWindow(hwnd, nCmdShow);
UpdateWindow(hwnd);
// Call UpdateWindow to
ensure that the window is drawn
// Timer
SetTimer(hwnd, 1,
STATUS_UPDATE_INTERVAL1, NULL);
//SetTimer(hwnd, 2, STATUS_UPDATE_INTERVAL2,
NULL);
// Windows message pump
MSG msg = {};
while (GetMessage(&msg,
NULL, 0, 0))
{
TranslateMessage(&msg);
DispatchMessage(&msg);
// Add a short delay
Sleep(SLEEP_TIME);
}
return 0;
}
Create a
Windows Project with MS
Visual Studio 2022 and add the headers and source files to the project.
Experimenting with the integrated debugger is ideal.
Download Link for C++ files and sounds

Instructions for creating the program using MS VS
2022: You should start with an empty project and configure it correctly. Here’s
how you can do it:
Create a New Project:
File ->
New ->
Project.
Empty Project and click
Next.Create.Configure Project Settings:
Solution Explorer
and select Properties.
Configuration Properties, navigate
to Linker
-> System.
Subsystem
from Console
to Windows.Add Preprocessor Definitions:
Properties
window, navigate to C/C++
-> Preprocessor.
_CONSOLE from the
Preprocessor Definitions
field.
Main.cpp, ...
Files:Solution Explorer.
Add ->
Existing Item....Main.cpp, ...
files, select it, and click Add.
Ctrl + Shift + B to build your
project.F5
to run your project.
If you prefer to modify the
.vcxproj file
manually, here is an example of what the relevant sections might look like after
changes:
<ItemGroup>
<PropertyGroup>
<LinkIncremental>true</LinkIncremental>
</PropertyGroup>
<PropertyGroup
Condition="'$(Configuration)|$(Platform)'=='Debug|x64'">
<LinkIncremental>true</LinkIncremental>
<GenerateManifest>true</GenerateManifest>
<SubSystem>Windows</SubSystem>
</PropertyGroup>
<PropertyGroup
Condition="'$(Configuration)|$(Platform)'=='Release|x64'">
<LinkIncremental>false</LinkIncremental>
<GenerateManifest>true</GenerateManifest>
<SubSystem>Windows</SubSystem>
</PropertyGroup>
</ItemGroup>
<ItemDefinitionGroup>
<ClCompile>
<PreprocessorDefinitions>_DEBUG;%(PreprocessorDefinitions)</PreprocessorDefinitions>
</ClCompile>
<Link>
<SubSystem>Windows</SubSystem>
</Link>
</ItemDefinitionGroup>
If there are still problems, search for "console" in the
vcxproj file and replace it with "Windows" for Subsystem and delete it in the
preprocessor definitions.
Have fun!